Selection of Raymond mill specifications and models
The selection of Raymond mill requires a comprehensive consideration of material properties, production capacity requirements and equipment performance, matching wear-resistant structure with efficient energy-saving design, and choosing mainstream brands with mature technology to achieve efficient production and long-term cost optimization.
Raymond mills are widely used in the mining, building materials, chemical, food, and pharmaceutical industries. The choice of model directly impacts production efficiency, product quality, and long-term operating costs. Choosing the right model requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as material properties, production requirements, equipment performance, and supplier capabilities. This article provides a comprehensive selection guide, combining technical specifications, application scenarios, and practical experience.
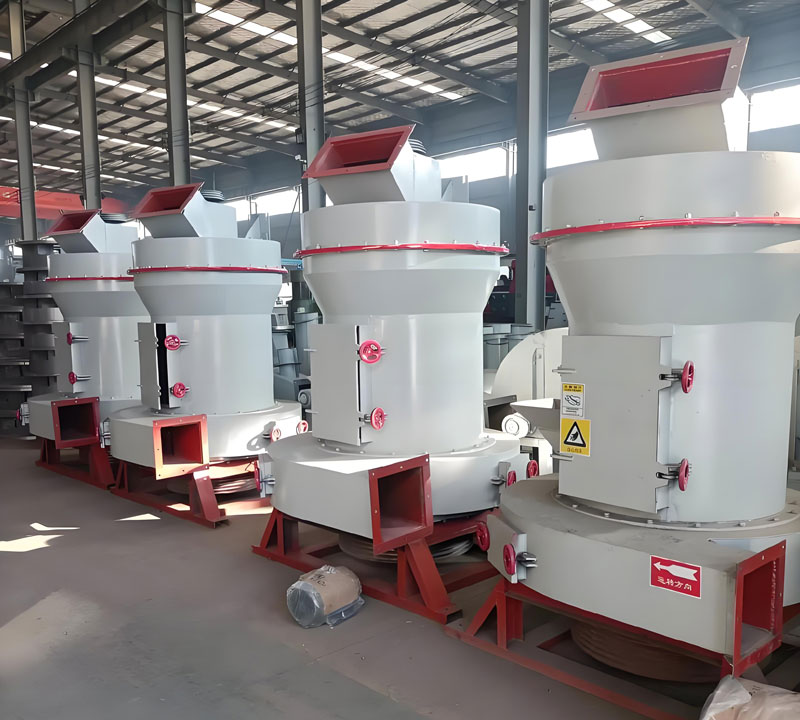

Clarify usage requirements
1. Material property analysis
● Hardness and Mohs Hardness: Different materials have different hardnesses (e.g., quartz is hard, talc is soft). Materials with a hardness of 7 or higher require a more wear-resistant model (e.g., the 5R/6R series equipped with wear-resistant alloy grinding rollers and rings) to avoid excessive wear.
● Humidity and particle size: Materials with a humidity greater than 6% tend to stick together, so you need to select a machine with a drying function or pre-treatment equipment. The feed particle size is generally ≤30mm. If the raw material lumps are too large, you need to use a jaw crusher or other pre-treatment equipment.
● Flammability and explosiveness: When handling coal and chemical raw materials, explosion-proof equipment must be selected to ensure safe production.
2. Production capacity and fineness requirements
● Capacity requirements: Select the corresponding model based on daily processing volume or hourly output (such as 15 tons/hour). For example, GK1720A is suitable for 15 tons/hour limestone desulfurization powder production.
● Fineness range: Standard models can be selected for conventional needs (80-400 mesh). High-precision grading systems or secondary grading equipment are required for special fineness (such as ultrafine powder ≤0.025mm).
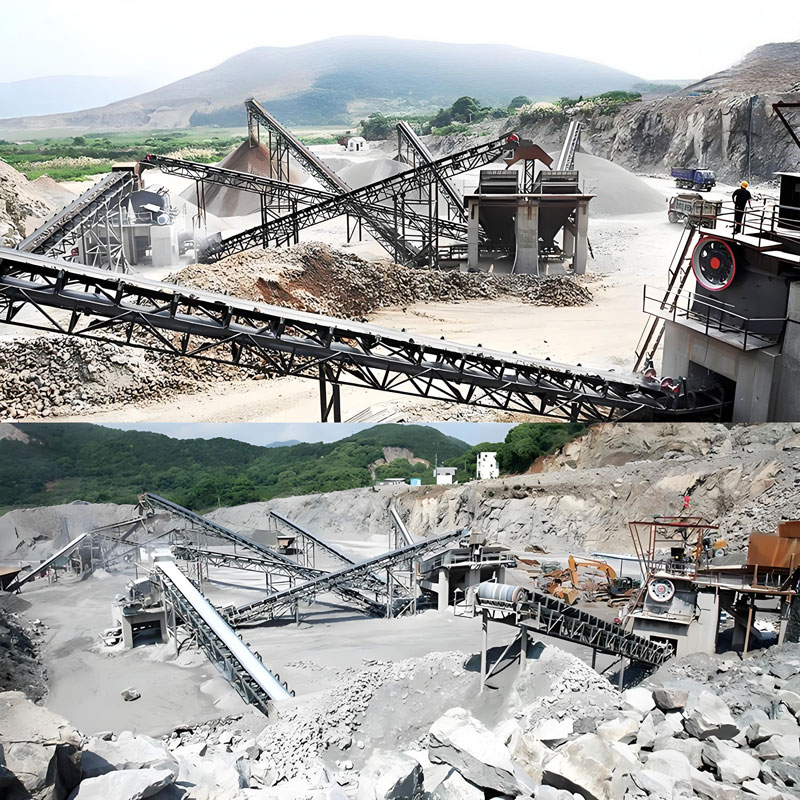

Matching of equipment performance and technical parameters
1. Host structure and core parameters
● Grinding roller and grinding ring configuration: Models such as 5R4119 are suitable for medium hardness materials, and GK1850 (larger grinding ring diameter) is suitable for large-scale production.
● Motor power and energy consumption: Compare the power of the main engine, fan, and classifier, and give priority to high-efficiency and energy-saving models (e.g., new equipment reduces energy consumption by 40%).
● Screening rate and output: High screening rate models (such as screening rate ≥99%) can reduce circulation load and improve efficiency.
2. Wear resistance and stability
● Material selection: Grinding rollers and grinding rings are preferably made of wear-resistant alloy materials (lifespan is three times that of traditional materials) to reduce replacement frequency.
● Structural innovation: New equipment such as “grinding roller assembly” and “multi-layer sealing structure” can extend maintenance cycles and reduce downtime.
Application Scenarios and Special Requirements
1. Industry-specific selection
● Mining/Building Materials: For processing high-hardness/large-scale materials such as iron ore and limestone, give priority to large models (such as the 6R series) and supporting pre-treatment equipment.
● Chemical/Food: When high requirements are placed on fineness and purity, choose high-precision classifiers and sealing equipment, and the materials must meet hygiene standards (such as food-grade stainless steel).
● Environmental protection/energy: Coal pulverizing requires explosion-proof design, and biomass energy processing needs to adapt to the characteristics of fiber materials.
2. Site and layout constraints
● Floor space: Small production lines can choose vertical structure models (small footprint, self-contained system), large factories can choose high-yield equipment with modular layout.
Supplier Evaluation and Long-term Guarantee
1. Brand and technical strength
● Give priority to large manufacturers with technological innovation capabilities (such as providing high-efficiency and energy-saving technologies) to avoid equipment quality and after-sales risks of small manufacturers.
● Verify equipment certification (such as CE, ISO) and industry application cases.
2. After-sales service and cost
● Confirm whether the supplier provides full-cycle services such as installation training, regular return visits, and spare parts supply.
● Comprehensively compare the price and long-term maintenance costs. High cost performance does not equal low price. It is necessary to weigh the initial investment and long-term benefits.
Practical Suggestions for Selection
1. Data provision and customized solutions: Provide suppliers with material samples, fineness requirements, and production targets, and obtain professional selection reports (e.g., leave a comment in the comments section for consultation).
2. On-site inspection and trial operation: Visit the supplier’s factory or customer’s site to verify the equipment’s operational stability and effectiveness.
3. Clear contract terms: stipulate equipment parameters, warranty period, and after-sales response time to avoid risks of hidden terms.
Related Products
Inquiry
Please leave us your requirements, we will contact you soon.